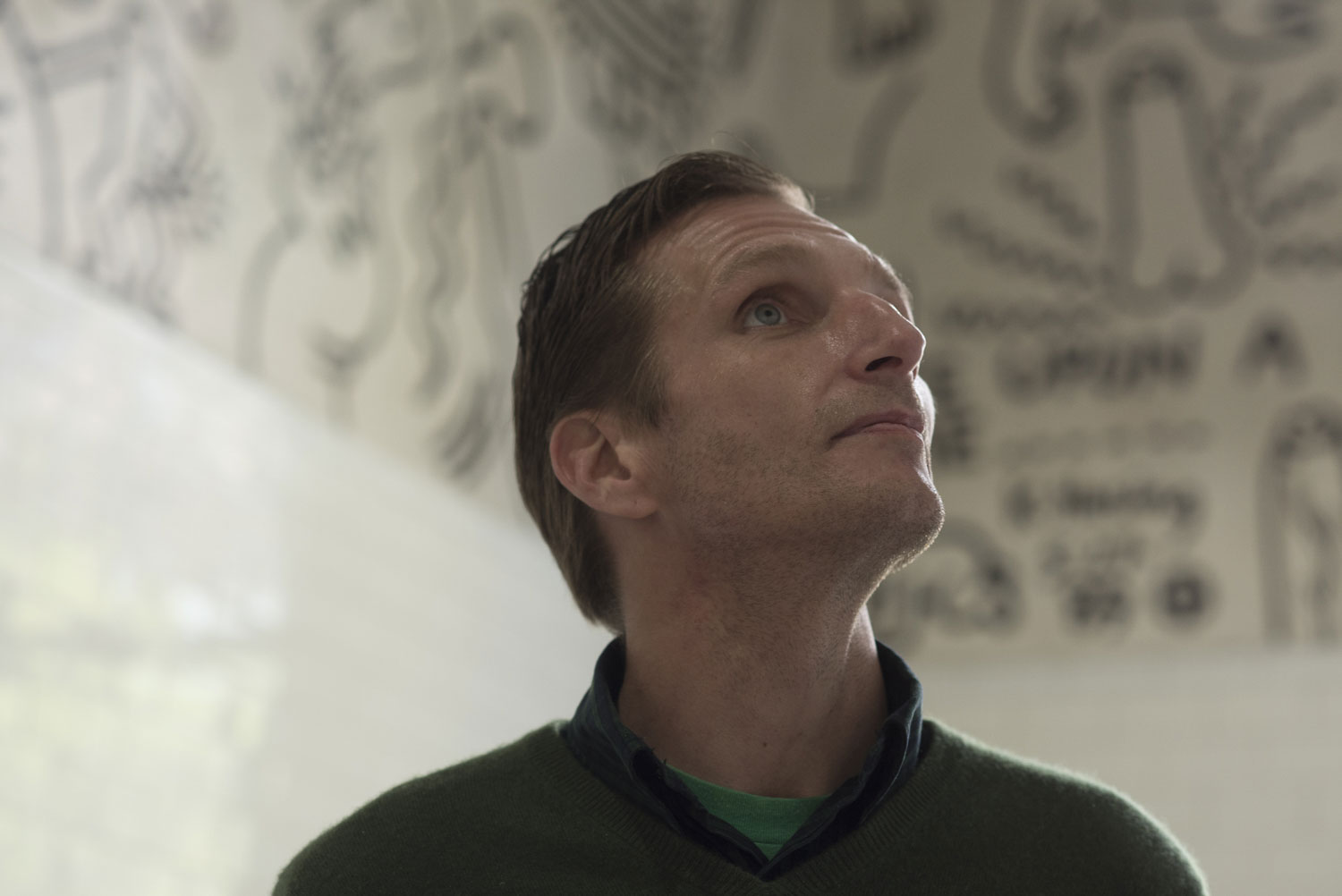

Jimmie Orr, 41
An overwhemling fear of a slow, lonley death from HIV lead Orr down the path to crystal meth.
Listen to Orr share his experience with addiction below.
I got lost in that place that crystal can take you to.
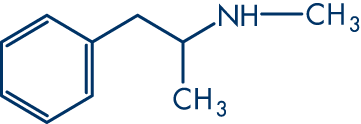
Methamphetamines
| Street Price |
|---|
| $100-300 per gram |
| Addictiveness Potential |
| 1.67 (not separated from Amphetamines in scale) |
Usage Rates
In 2011 2.8 percent of New York City high school students reported having used methamphetamine one or more times in their life. (NYC DHMH)
Origin/Synthesis
Amphetamine was first synthesized at Universität Berlin by Romanian chemist Lazar Edeleanu in 1887. Methamphetamine was not sythesized until 1919 by Japanese chemist A. Ogata. During World War II, methamphetamine and amphetamine are used by Allied and Axis countries to improve troop performance. Japan and Germany extensively used methamphetamine.
In 1940, methamphetamine is first marketed as "Methendrine" by pharmaceutical company Burroughs Wellcome. Twenty years later, illict production begins as the Attorney General of California requests that injectable versions are removed from the market. As use rises in the United States, congress passes the Drug Abuse Control Amendment, prohibiting the nonregistered manufacture, sale and possession of methamphetamine with other stimulants. In 1970, methamphetamine in classified as a Schedule II drug in the U.S.
Highs & Lows
Highs
Physical
- Increased energy and alertness
- Decreased need for sleep
- Decreased appetite
- Excessive talking
Mental
- Increased sociablity
- Mild to extreme mood lift
- Euphoria
- Increased sexuality

Lows
Physical
- Weight loss, Sweating
- Tightened jaw muscles
- Disrupted sleep patterns
- Reduced enjoyment
- Itching
- Welts on skins
- Nausea, vomitting, diarrhea
- Dry mouth
- Tooth decay
- Shortness of breath
- Twitching
- With extreme use: fatal kidney, liver and lung disorders
- Possible brain damage
- Lowered resistance to illness
- Stroke and cardiovascular disease
Mental
- Visual and auditory hallucinations
- Moodiness and irritability
- Anxiousness
- Nervousness
- Paranoia
- Ego-inflation and false sense of confidence
- Agressive and violent behavior
- Extreme depression and suicidal tendencies