
John Lesko
Lesko, a Vietnam veteran, can't imagine a life without drugs. He recently overdosed on his drug of choice, heroin.
Listen to Lesko describe his battle with PTSD and addition below.
I have to keep it down to a dull roar as far as my use goes, but you know that's just the way I am.
Heroin
| Street Price |
|---|
| $40-350 per gram, depending on quality |
| Addictiveness Potential |
| 3.00 |
Usage Rates
Fifty percent increase in Mexico's opium production last year, according to the New York Times.
In 2013, heroin was involved in 54 percent of all overdose deaths, making it the most common substance involved in overdose deaths.
The rate of overdose deaths involving heroin increased for three consecutive years from 3.1 per 100,000 New yorkers (209 deaths) in 2010 to 6.2 per 100,000 New Yorkers (424 deaths) in 2013. (NYC Office of the Chief Medical Examiners and NYC DOHMH Bureau of Vital Statistics).
Origin/Synthesis
First synthesized in 1878, Heroin is a later synthesis of morphine. Morphine and codeine were synthesized from opium in 1805. Opium has been in use since 3400 BCE in Sumeria, which referred to it as Hul Gil, the "joy plant." In 1898 Bayer Pharmaceutical began synthesizing heroin commercially. It was used as an alternative to morphine which was increasingly being abused.
Highs & Lows
Highs
Physical
- Pain Ignorance and relief
- Heroin is converted back into morphine, which binds to molecules on cells known as opioid receptors
- Opioid receptors located in the brain stem control automatic processes critical for life
Mental
- Euphoria
- Safe and warm feelings
- Calmer, less uptight and lonely
- A kind of floating, dream-line state
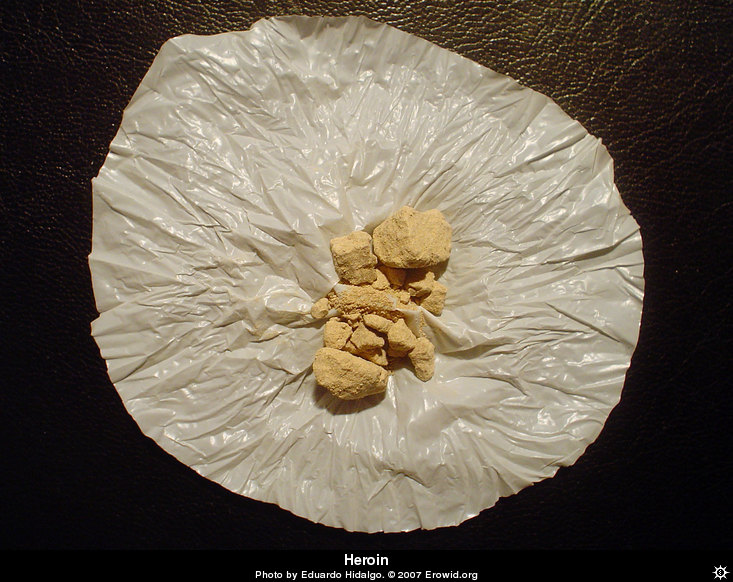

Lows
Physical
- suppression of breathing
- reduce sex drive
- increase sexual arousal
- tolerance develops quickly
- the risk of addiction is very high
- harsh withdrawal
- dry mouth
- a warm flushing of the skin
- heaviness of the extremities
- Increased risk of contraction of blood bourne illnesses like hepatitis-c and HIV
Mental
- clouded mental functioning
- strong cravings to be high when not